|
In Canada there are three types of caribou - the barren-ground caribou, Peary caribou and woodland caribou.
Woodland caribou live in mature forests. Some woodland caribou live in the foothills and mountains and are also called mountain caribou.
Woodland caribou were once found across the northern hemisphere.
Today their numbers have greatly declined because of loss of habitat, disturbance of their habitat, overhunting, predators and disease (brain worm).
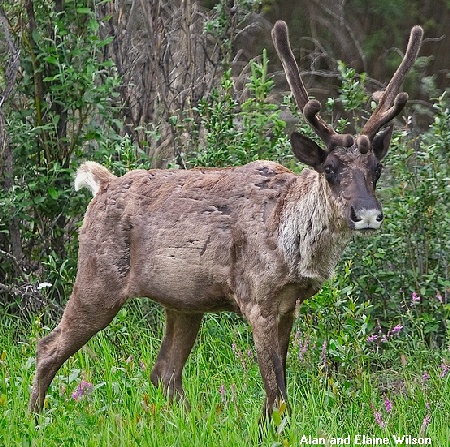 photo - male mountain caribou, courtesy of Alan and Elaine Wilson, Nature's Pics Online
photo - male mountain caribou, courtesy of Alan and Elaine Wilson, Nature's Pics Online
license - Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
DESCRIPTION
- a member of the deer family
- larger, heavier and darker in colour than the barren-ground caribou
- weight adult males (bulls) average 200 kg (440 lb)
- females (cows) are smaller; 115 kg to 135 kg (250 lbs to 300 lbs)
- length average 6.5 to 7.5 feet (2 to 2.3 meters)
- height to shoulder 1.2 m (4 ft) to 1.5 m (5 ft)
- only member of deer family in which both males and females grow antlers
- forward-curving antlers may spread to 1.5 m wide (5 ft).
- cows' antlers are shorter, not as many branches
- males shed antlers in the fall
- females shed antlers in spring after calves are born
- large feet with wide hooves
- light grey winter coat, long hairs
- dark brown summer coat, short hairs
- darker fur over face, back and sides
- cream-coloured around neck, chest, belly, tail, rump and above each hoof
- males have thick white manes under their necks

woodland caribou, courtesy of Troy B. Thompson, Flickr.com
Creative Commons license
Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 Generic
HABITAT/RANGE
- HABITAT:
-mature forests, muskeg and bogs
-old growth forests (over 100 years old) containing tree lichens, the main winter food source of caribou
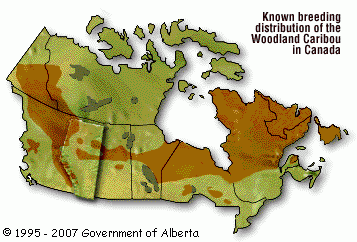
- RANGE:
- northern forests (from British Columbia and Yukon Territory to Newfoundland and Labrador) and forested foothills and mountains
FOOD
- Ground and tree lichens are the main source of food.
- They also eat mosses, sedges, grasses and leaves of the willow and birch.
- Caribou are cud-chewing animals (like cows).
- There are four chambers in the stomach to help break down food.
- They chew, swallow, regurgitate and chew again.
Reindeer moss is an important lichen for the woodland caribou

photo credit - L. Schneider ; license - Creative Commons
ADAPTATIONS
- long thick winter coat with two layers of fur
- top coat of hollow hairs provides excellent insulation from the cold
- ears and muzzle (nose) are covered with fur
- short, thick muzzle reduces heat loss when breathing in and out
- short ears, small tail to reduce heat loss
- long legs, large feet with crescent-shaped hooves for walking in deep snow or bogs
- digs lichens out of the snow with sharp-edged hooves
- excellent sense of smell to find lichens under the snow
- feeds mainly on ground and tree lichens in the winter
HABITS / BEHAVIOR
- live in small groups
- do not migrate great distances, but stay within their range
- mountain caribou move up and down the mountain slopes
(from higher elevations to forested foothills and valleys)
- strong swimmers
- usually silent, but occasionally snort, bellow, pant and grunt
- bulls use their racks (antlers) to defend their group of cows
- adult bulls drop their antlers in November and December
- cows lose antlers when calving (May or June)
ENEMIES / PROTECTION
- prey for wolves, grizzly and black bears, cougars, wolverines, lynx, coyotes
- illegal to hunt woodland caribou in most provinces
- try to avoid swarms of biting insects in the summer
- pestered by mosquitoes, black flies, warble flies and nose bot flies
- constant twitching, movement and blood loss weakens the animals
THE YOUNG
- Calves are born late May or early June.
- A cow gives birth to one calf.
- The calf is born away from the herd.
- A calf can walk and run within two hours after birth.
 photo - young caribou, courtesy of Alan and Elaine Wilson, Nature's Pics Online
photo - young caribou, courtesy of Alan and Elaine Wilson, Nature's Pics Online
license - Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
OTHER FACTS
- 3.5 to 4 million worldwide
- some herds/subspecies have very low numbers
- between 40,000 to 50,000 in Canada's northern forests
- threatened or endangered in most provinces
- approximately 43 mountain caribou in Selkirk Mountains
(southern British Columbia and south of the border in northern states of Idaho and Washington)
- endangered in the United States in 1984
- male - bull; female - cow; baby - calf or fawn
- life span 10 - 15 years
- Logging of old-growth forests is one reason for their decline.
- Reindeer are close relatives of the caribou.
- A caribou is on the Canadian quarter.
BARREN-GROUND CARIBOU
|






